Products
Products
Cylindrical Generators
Generators specifically designed for small to medium enclosures
Box Type Generators
Compact fire suppression units specifically designed for confined spaces
HERO Generators
Portable devices that are designed to extinguish fire before it spreads
ATEX Generators
Designed for potentially explosive atmospheres and other hazardous areas
VELEX
Fire suppression for the protection of various types of vehicles
View all Products
Solutions
Solutions by Applications
FirePro system designs for its different applications across the world
Electrical Panels
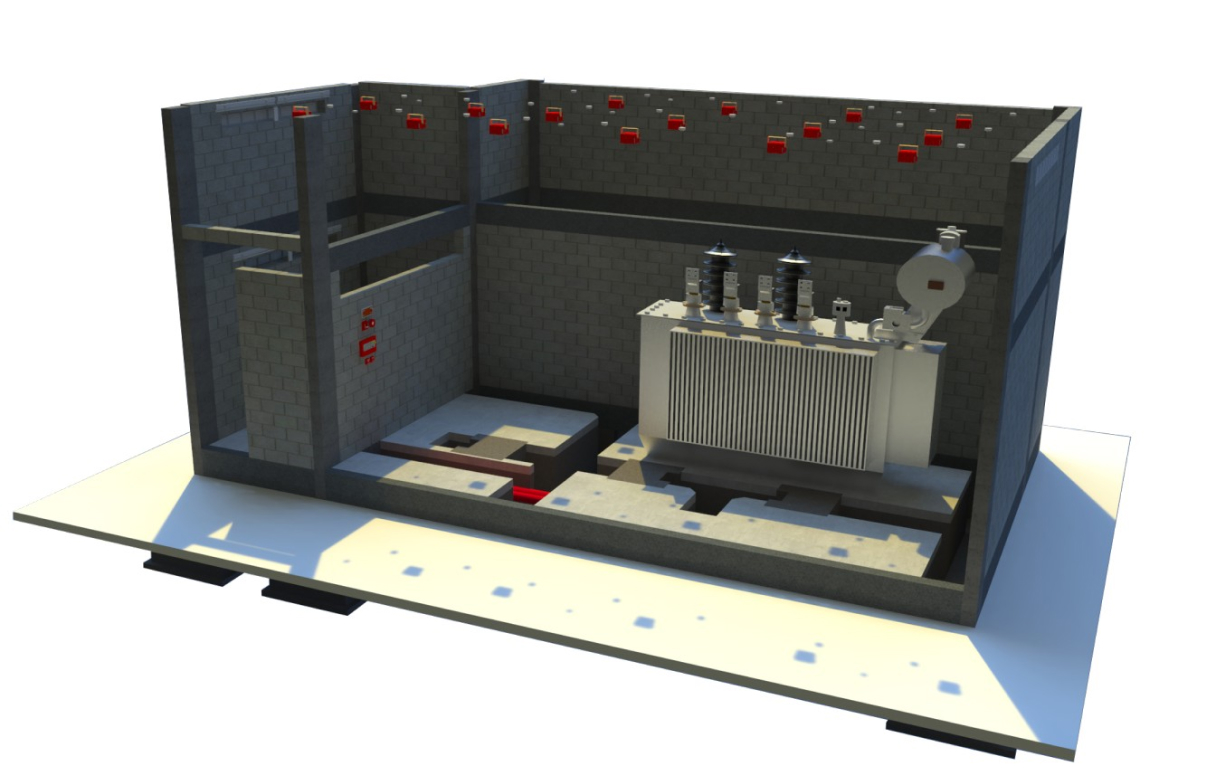
Power Transformers
Electrical Control Rooms
Energy Storage Systems
Electrical Diesel Generators
Lead-acid Battery Room
Archive Rooms
Solutions by Industries
How FirePro supports various industries and their issues with fire
Power Generation
Marine
Transportation
Renewable Energy
Oil & Gas
Warehousing
Defense
Mining
Case studies
Compliance

International Polar Foundation
Task in hand for International Polar Foundation..

Samsung SDI
Tecnology / Electrical Panels

Pfizer
Pharmaceuticals / Diesel Generator Machinery
View all case studies
About
Technology
FirePro system designs for its different applications across the world
Knowlege Base
Certificates & Trademarks
Technology
Environment
Distribution Network
FAQs
Media
Glossary
Company
FirePro system designs for its different applications across the world
Customers & Case Studies
Why choose FirePro?
About Us
Management Team
Careers
News
Contact Us